Outbreak Response
Sabin’s continues to set new benchmarks in responding to disease outbreaks for Marburg and Sudan ebolavirus.
Sabin’s current vaccine doses, developed with U.S. government funding, are owned by the U.S. government. Therefore, the U.S. must approve their release and donation for outbreak response. To begin the donation process, the affected country must formally request doses from the U.S. government, as Rwanda did during the 2024 outbreak.
Below are recent highlights of Sabin’s outbreak response.
Marburg Virus Outbreaks
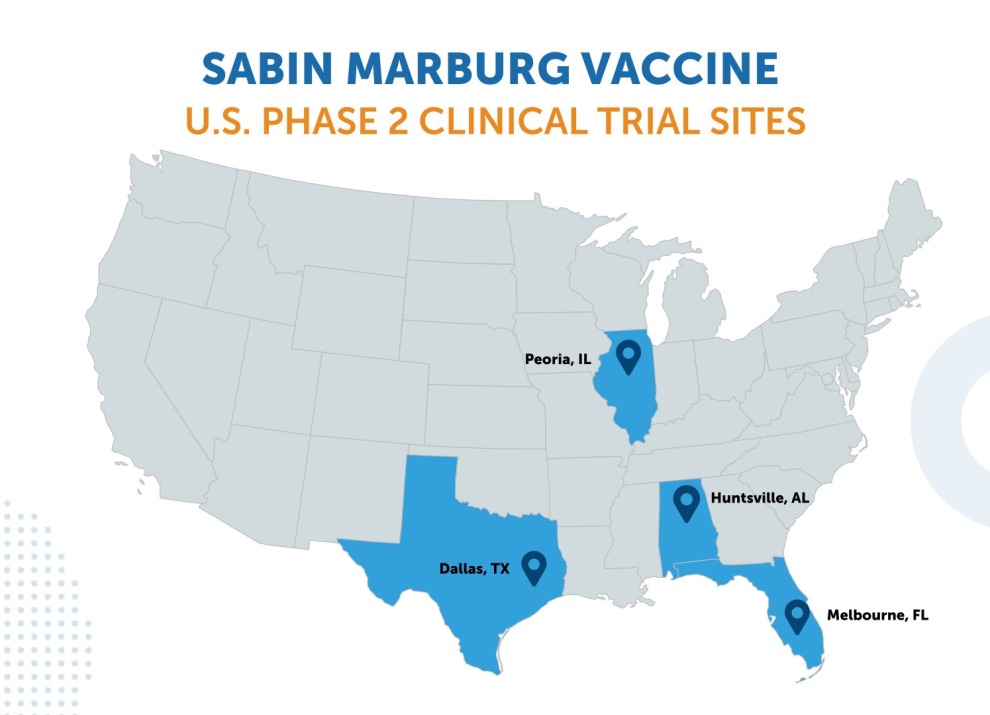
September-December 2024: Rwanda
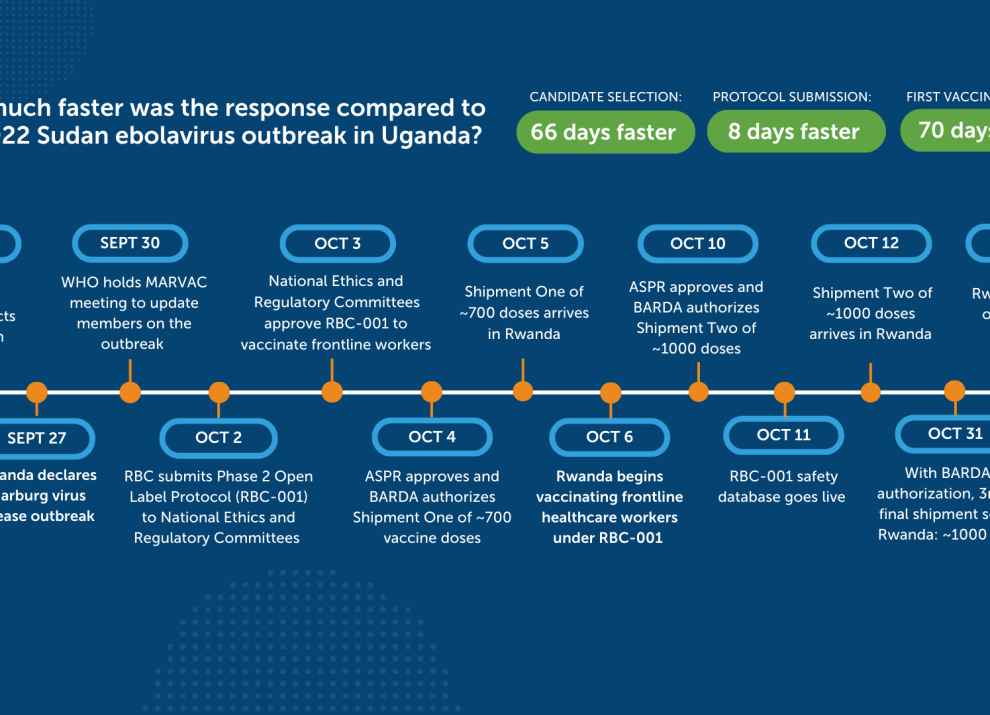
 During the 2024 Marburg outbreak in Kigali, Sabin’s investigational vaccines were administered within just ten days of the outbreak declaration. Sabin delivered more than 2,700 doses in three shipments to support a Phase 2 open-label trial for frontline workers, sponsored by the Rwanda Biomedical Centre. This was Rwanda’s first Marburg outbreak. The outbreak was announced on September 27, 2024, and declared over on December 20, 2024.
During the 2024 Marburg outbreak in Kigali, Sabin’s investigational vaccines were administered within just ten days of the outbreak declaration. Sabin delivered more than 2,700 doses in three shipments to support a Phase 2 open-label trial for frontline workers, sponsored by the Rwanda Biomedical Centre. This was Rwanda’s first Marburg outbreak. The outbreak was announced on September 27, 2024, and declared over on December 20, 2024.
February-June 2023: Tanzania and Equatorial Guinea
 During the 2023 outbreaks in these countries, Sabin’s vaccine was recognized by WHO as a top choice for deployment. Though those outbreaks ended before a trial could begin, Sabin ensured doses were ready, reinforcing its role in preparedness and rapid action. Tanzania declared its Marburg outbreak on March 21, 2023, and announced its end on June 2, 2023. Equatorial Guinea’s outbreak was announced on February 13, 2023, and declared over on June 8, 2023.
During the 2023 outbreaks in these countries, Sabin’s vaccine was recognized by WHO as a top choice for deployment. Though those outbreaks ended before a trial could begin, Sabin ensured doses were ready, reinforcing its role in preparedness and rapid action. Tanzania declared its Marburg outbreak on March 21, 2023, and announced its end on June 2, 2023. Equatorial Guinea’s outbreak was announced on February 13, 2023, and declared over on June 8, 2023.
Sudan Ebolavirus Outbreaks
September 2022-January 2023: Uganda
 In 2022, Sabin swiftly delivered investigational Sudan ebolavirus vaccine doses to Uganda—just 79 days after the outbreak was declared. While the outbreak ended before a planned clinical trial could began, Sabin’s vaccine was among three WHO-recommended candidates.
In 2022, Sabin swiftly delivered investigational Sudan ebolavirus vaccine doses to Uganda—just 79 days after the outbreak was declared. While the outbreak ended before a planned clinical trial could began, Sabin’s vaccine was among three WHO-recommended candidates.
Recommended for You

We make vaccines more accessible, enable innovation and expand immunization across the globe.